Now that I finished my last post about counting keywords in source code, I will give away the little script I did to help me with the counting. It definitively requires some improvements to cover some extra cases I did not consider, but it work just fine if you manage to avoid them... or even better, implement them yourself :D
1. Multi-line comments are not supported. If there are reserved words within the comments, they will be counted as keywords. But worry not; single line comments work fine.
2. Text literals are not supported. If there are reserved words within the string, they will be counted as keywords.
I think regular expressions can handle those 2 cases. I'll add those two features if I need them in the future.
The programming language used was Python version 3.1.3
I formatted some parts of the code to correctly display it using the size limit of this blog's page. For instance, if the script doesn't compile; try using one line comma separated lists and if statements.
I think the code is simple and very easy to read... that's what all programmers say about their own code, right? Anyway, here below, I will begin by showing, function by function, the code of the script including lots of unnecessary comments and some screen shots that help explain what it does. Next, I will show a complete example of how to use it and the output.
The complete script without comments it's available at the bottom of this post.
Dissecting the Script
# import from sys to handle script's (command line) parameters
import sys
# get_line_comment_char function returns the Language's single
# line character(s)
# only one "single comments character" is taken in consideration
# even if the language supports multiple single line comments
# I grouped languages using the same comment character to reduce
# the number of ifs
def get_line_comment_char(language):
language = language.lower()
if language in ('c#', 'csharp', 'cpp', 'cppcli', 'c++', 'c++cli', 'f#',
'fsharp', 'boo', 'phalanger', 'php', 'delphiprism', 'delphi',
'nemerle', 'groovy', 'java', 'fantom', 'fan', 'jscript',
'jscriptnet', 'scala', 'javafx', 'javafxscript', 'gosu'):
return '//'
elif language in ('vb', 'vbnet', 'visualbasic'):
return '\''
elif language in ('jython', 'ironpython', 'python', 'jruby', 'ironruby',
'ruby', 'cobra'):
return '#'
elif language in ('zonnon'):
return '(*'
return None
Example:
# get_language_keywords function returns a list of all the
# keywords (reserved words) for the given language
# except for the primitive types since I didn't consider them
# as keywords for my comparison purposes
# if you need them, you can take the complete keywords lists
# this blog's Keywords page
# I removed the lists to save space because it makes the program
# too long and less readable, so, in the function below,
# for every ocurrence of keywords = '' you change '' with the list
# of keywords of that language.
def get_language_keywords(language):
language = language.lower()
if language == 'c#' or language == 'csharp':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'vb' or language == 'vbnet'
or language == 'visualbasic':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'cpp' or language == 'cppcli'
or language == 'c++' or language == 'c++cli':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'f#' or language == 'fsharp':
keywords = ''
elif language == "boo":
keywords = ''
elif language == 'phalanger' or language == 'php':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jython' or language == 'ironpython'
or language == 'python':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jruby' or language == 'ironruby'
or language == 'ruby':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'delphiprism' or language == 'delphi':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'zonnon':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'nemerle':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'groovy':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'java':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'cobra':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'fantom' or language == 'fan':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jscript' or language == 'jscriptnet':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'scala':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'javafx' or language == 'javafxscript':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'gosu':
keywords = ''
else:
keywords = ''
return keywords.split()
Example:
# is_keyword function returns true if the given keyword is a
# valid keyword in the given language
def is_keyword(key, language_keys):
if key in language_keys:
return True
return False
Example:
# remove_special_characters function removes special characters
# from the given text and returns the resulting sequence
# special characters includes open and closing blocks,
# operators, and so on (see the list below).
def remove_special_characters(text):
special_characters = ('(','[','{','}',']',')','+','-','*','/','=','^','&',
'%','$','#','@','!','~','\'','\"', '?', '>', '<', ':',
';', ',', '.')
for character in special_characters:
text = text.replace(character, ' ')
return text
Example:
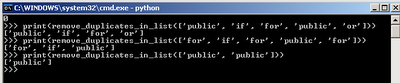
# remove_duplicates_in_list function removes any duplicate value
# found in the given sequence and returns the resulting sequence
def remove_duplicates_in_list(sequence):
# Thanks to Dave Kirby for this function taken from comments in
# http://www.peterbe.com/plog/uniqifiers-benchmark
seen = set()
seen_add = seen.add
return [x for x in sequence if x not in seen and not seen_add(x)]
Example:
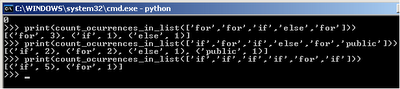
# count_ocurrences_in_list function returns a new list of paired values
# that contain the keyword and how many times it appeared in the code
# using the standard count method of the sequences types
def count_ocurrences_in_list(sequence):
totals_by_word = []
no_duplicates = remove_duplicates_in_list(sequence)
for word in no_duplicates:
totals_by_word.append((word,sequence.count(word)))
return totals_by_word
Example:
# print_results function prints the given sequence to the console
# It displays the list of Keyword and Total Number of Keywords
def print_results(sequence):
print('', end='\n')
for item in sequence:
print('%s, %s' % (item[0], item[1]))
Example:
# print_to_file function creates an output file and prints the given
# sequence into it.
# It writes the list of Keyword and Total Number of Keywords
def print_to_file(sequence, output):
with open(output, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as output_file:
output_file.write('\n')
for item in sequence:
output_file.write('%s, %s\n' % (item[0], item[1]))
Example:
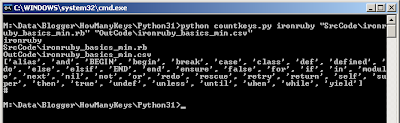
Output:
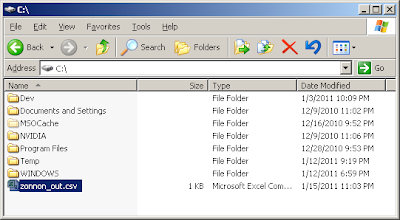
Opening CSV:
# Main function. The program's entry point.
def main(argv=None):
# if command line arguments are not empty
if argv is None:
# assign them to the local sequence variable argv
argv = sys.argv
# validate the script was used correctly.
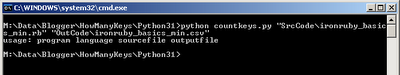
if len(argv) != 4:
# Otherwise, print the usage message to the console
print("usage: program language sourcefile outputfile")
# and exit the script
sys.exit()
Example:
# get command line arguments
# parameter 2 should be the language of the source code you want to count
programming_language = sys.argv[1]
# parameter 3 should be the file that contains the source code you want to count
source_file = sys.argv[2]
# parameter 4 should be the file that will contain the counting results
output_file = sys.argv[3]
# get the list of reserved words for the given programming language
language_keywords = get_language_keywords(programming_language)
# get the single line comment character for the given programming language
comment_character = get_line_comment_char(programming_language)
Example:
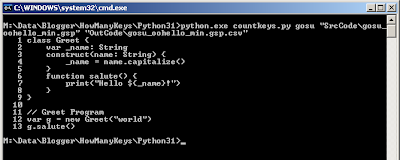
Here I added some print() and exit() to stop execution of the script
# define a variable that will hold the total number of keywords found in the file
total_keywords_found = 0
# define a list that will store all valid language keywords found in the file
list_of_keywords_found = []
line_number = 0
# open a file as read only (default mode)
with open(source_file, encoding='utf-8') as source_code:
# navigate through the lines of the file
for line in source_code:
# get the line number. Used only for console display purposes
line_number += 1
Example:
The following line adds the line number to the beginning of the line being read
print('{:>4} {}'.format(line_number, line.rstrip()), end='\n')
# remove line comment if there is one based on the
# language's single line comment character
comment_idx = line.find(comment_character)
if comment_idx >= 0:
line = line[0:comment_idx]
Example:
# remove special characters from remaining text in line
# (operators and open-close characters)
line = remove_special_characters(line)
# create a list with all remaining words in the line
words = line.split()
Example:
# navigate through the words of the sequence
for word in words:
# if the current word is a valid keyword for the
# given language
if is_keyword(word, language_keywords):
# add to the list of
# "total keywords found in the source code" the word
list_of_keywords_found.append(word)
# increment the number of total words found
# in the source code
total_keywords_found = total_keywords_found + 1
Example:
# define a list that will store all paired
# values (keyword and total ocurrences of that keyword)
totals_to_output = []
# insert first pair of values as the first element of the list,
# that is the Programming Language and the Total Keywords found
totals_to_output.append((programming_language.capitalize(),str(total_keywords_found)))
# insert all other pairs of values (keyword and total ocurrences
# of that keyword) found on the source code
totals_to_output.extend(count_ocurrences_in_list(list_of_keywords_found))
Example:
# print the results to the console
print_results(totals_to_output)
# print the results to the output file
print_to_file(totals_to_output, output_file)
# run the program
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Example:
Using the Script
How to use is was already shown in the step by step example above, but here below I just show you how I did the counting for my previous post "Keywords in source code Round 2"
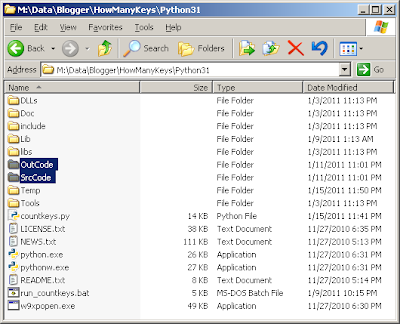
First I created 2 folders:
1. SrcCode
2. OutCode
Then, I added all the source code files I wanted to count from into the SrcCode folder.
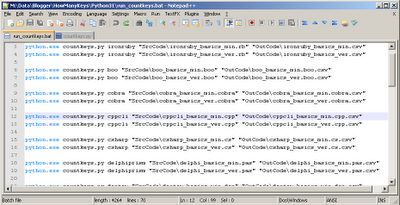
Next step was to create a batch file that runs the python script for all the files in the SrcCode folder.
And ran it
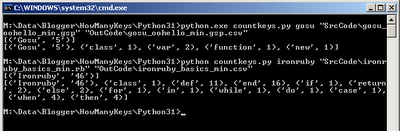
Console Output
Files Output in folder OutCode
Et Voilà! I then started merging together the results and did the graphs.
Hope this script works for you or at least shows you some cool python features :)
Final Script
Just don't forget to add the language keywords! take them from the Keywords Page.
Example:
keywords = 'public private static internal for if else while switch'
import sys
def get_line_comment_char(language):
language = language.lower()
if language in ('c#', 'csharp', 'cpp', 'cppcli', 'c++', 'c++cli', 'f#',
'fsharp', 'boo', 'phalanger', 'php', 'delphiprism', 'delphi',
'nemerle', 'groovy', 'java', 'fantom', 'fan', 'jscript',
'jscriptnet', 'scala', 'javafx', 'javafxscript', 'gosu'):
return '//'
elif language in ('vb', 'vbnet', 'visualbasic'):
return '\''
elif language in ('jython', 'ironpython', 'python', 'jruby', 'ironruby',
'ruby', 'cobra'):
return '#'
elif language in ('zonnon'):
return '(*'
return None
def get_language_keywords(language):
language = language.lower()
if language == 'c#' or language == 'csharp':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'vb' or language == 'vbnet'
or language == 'visualbasic':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'cpp' or language == 'cppcli'
or language == 'c++' or language == 'c++cli':
keywords = ''
elif language == "f#" or language == "fsharp":
keywords = ''
elif language == "boo":
keywords = ''
elif language == 'phalanger' or language == 'php':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jython' or language == 'ironpython'
or language == 'python':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jruby' or language == 'ironruby'
or language == 'ruby':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'delphiprism' or language == 'delphi':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'zonnon':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'nemerle':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'groovy':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'java':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'cobra':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'fantom' or language == 'fan':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'jscript' or language == 'jscriptnet':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'scala':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'javafx' or language == 'javafxscript':
keywords = ''
elif language == 'gosu':
keywords = ''
else:
keywords = ''
return keywords.split()
def is_keyword(key, language_keys):
if key in language_keys:
return True
return False
def remove_special_characters(text):
special_characters = ('(','[','{','}',']',')','+','-','*','/','=','^','&',
'%','$','#','@','!','~','\'','\"', '?', '>', '<', ':',
';', ',', '.')
for character in special_characters:
text = text.replace(character, ' ')
return text
def remove_duplicates_in_list(sequence):
seen = set()
seen_add = seen.add
return [x for x in sequence if x not in seen and not seen_add(x)]
def count_ocurrences_in_list(sequence):
totals_by_word = []
no_duplicates = remove_duplicates_in_list(sequence)
for word in no_duplicates:
totals_by_word.append((word,sequence.count(word)))
return totals_by_word
def print_results(sequence):
print('', end='\n')
for item in sequence:
print('%s, %s' % (item[0], item[1]))
def print_to_file(sequence, output):
with open(output, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as output_file:
output_file.write('\n')
for item in sequence:
output_file.write('%s, %s\n' % (item[0], item[1]))
def main(argv=None):
if argv is None:
argv = sys.argv
if len(argv) != 4:
print("usage: program language sourcefile outputfile")
sys.exit()
programming_language = sys.argv[1]
source_file = sys.argv[2]
output_file = sys.argv[3]
language_keywords = get_language_keywords(programming_language)
comment_character = get_line_comment_char(programming_language)
total_keywords_found = 0
list_of_keywords_found = []
line_number = 0
with open(source_file, encoding='utf-8') as source_code:
for line in source_code:
line_number += 1
comment_idx = line.find(comment_character)
if comment_idx >= 0:
line = line[0:comment_idx]
line = remove_special_characters(line)
words = line.split()
for word in words:
if is_keyword(word, language_keywords):
list_of_keywords_found.append(word)
total_keywords_found = total_keywords_found + 1
totals_to_output = []
totals_to_output.append((programming_language.capitalize(),str(total_keywords_found)))
totals_to_output.extend(count_ocurrences_in_list(list_of_keywords_found))
print_results(totals_to_output)
print_to_file(totals_to_output, output_file)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()



















Thaank you for writing this
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDelete